Monday, 28 May 2012
Monday, 14 May 2012
Customer Relationship management & Business Intelligence - Week Eleven Questions
Data mining is the process of analysing data to extract
information not offered by the raw data alone. Data mining can begin at a
summary information level and progress through increasing levels of detail or
the reverse. Data mining is the primary tool used to uncover business
intelligence in vast amounts of data.
Wednesday, 9 May 2012
Operations Management and Supply Chain - Week Nine Questions
1.
Define the term
operations management
1) Plan – Strategic portion of supply chain management. A company must have a plan for managing all the resources that go towards meeting customer demand for products or services. A significant part of planning is developing a set of metrics to monitor the supply chain so that it is efficient, effective, costs less, and delivers high quality and value to customers.
 3) Make – Companies must manufacture their
products or services. This can include scheduling the activities necessary for
production, testing, packaging, and preparing for delivery. This is the most
metric-intensive portion of the supply chain, measuring quality levels,
production output and worker productivity.
3) Make – Companies must manufacture their
products or services. This can include scheduling the activities necessary for
production, testing, packaging, and preparing for delivery. This is the most
metric-intensive portion of the supply chain, measuring quality levels,
production output and worker productivity.
Operations management (OM) is the management of systems or
processes that convert or transform resources (including human resources) into
goods and services.
2.
Explain operations
management’s role in business
Operations management is responsible for managing the core
processes used to manufacture goods and produce services.
3.
Describe the correlation
between operations management and information technology
Information technology enables businesses
to differentiate themselves from competitors to gain competitive advantage and
works to maximise the efficiency of IT operations so that the business can
focus on their resources on providing value for the business. In conjunction to
this operations management ensures that these efficiencies of IT operations are
conducted as a result of being the core processes used to manufacture goods and
produce the services.
4.
Explain supply chain management
and its role in a business
Supply chain management (SCM) involves the management of
information flows between and among stages in a supply chain to maximise total
supply chain effectiveness and profitability.
5.
List and describe the
five components of a typical supply chain1) Plan – Strategic portion of supply chain management. A company must have a plan for managing all the resources that go towards meeting customer demand for products or services. A significant part of planning is developing a set of metrics to monitor the supply chain so that it is efficient, effective, costs less, and delivers high quality and value to customers.
2) Source – Companies must carefully
choose reliable suppliers that will deliver goods and services required for
making products. Companies must endeavour to develop a set of pricing,
delivery, and payment processes with suppliers and create metrics for
monitoring and improving the relationships.
4) Deliver – Commonly referred to as
logistics. It is the set of processes that plans for and controls the efficient
and effective transportation and storage of supplies from suppliers to
customers. During this, companies must
ensure they are able to receive orders from customers, fulfil the order via a
network of warehouses, pick transportation companies to deliver the products,
and implement a billing and invoicing system to facilitate payments.
5) Return – This is typically the most
problematic step in the supply chain, companies must ensure they create a
network for receiving defective and excess products and support customers who
have issues with delivered products.
Networks & Wireless - Week Nine Questions
1.
Explain
the business benefits of using wireless technology.

2. Describe the business benefits associated with VoIP
3. Compare LANs and WANs
4. Describe RFID and how it can be used to help make a supply chain more effective.
5. What is one new emerging technology that could change a specific industry
Wireless
technology refers to any type of electoral or electronic operations that is
accomplished without the use of a ‘hard wired’ connection and is a means of
linking computers using infrared or radio signals.. The benefit of utilising
wireless technology is cost effective, companies/residents no longer have to
rip up buildings or streets or lay down expensive cables. Wireless technology
has obvious advantages for people on the move who would like access to the
internet in airports, restaurants and hotels.
2. Describe the business benefits associated with VoIP
Voice over IP (VoIP) uses TCP/IP technology to transmit voice calls over
Internet technology. The telecommunications industry has experienced excellent
benefits from combining VoIP with emerging standards that allow for easier
development, interoperability among systems and application integration.
3. Compare LANs and WANs
A local area network (LAN) is designed to connect a group of computers
in close proximity to each other such as in an office building, a school or a
home. A LAN is useful for sharing resources like files, printers, games, or
other application. It often connects to other LANs and to the internet or wide
area networks. In contrast to this local area network, a wide area network
(WAN) spans a large geographical area, such as a state, province or country.
WANs connect multiple smaller networks, such as local area networks.
4. Describe RFID and how it can be used to help make a supply chain more effective.
Radio frequency identification (RFID) technologies use active or passive
tags in the form of chips or smart label that can store unique identifiers and
relay this information to electronic readers. RFDI tags can cut costs by
requiring fewer workers fir scanning items; they also can provide more current
and more accurate information to the entire supply chain.
5. What is one new emerging technology that could change a specific industry
An emerging technology that could potentially change the way in which Wi-Fi
access operates is WiMAX, this can solve all of the issues involved with Wi-Fi
such as:
-
Small
hotspots, and as a result coverage is sparse.
This evolving technology can cover an area of as much as 48,000 square
kilometres, depending on the number of users.
Sunday, 6 May 2012
Databases and Data Warehouses - Week seven Questions
1. List, describe, and provide an example of each of the five
characteristics of high quality information.
Accuracy – Are all the values correct? For example, is the name spelled correctly? Is
the dollar amount recorded properly?
Completeness – Are any of these values missing? For example, is the address complete
including street, city, state and postcode?
Consistency – Is aggregate or summary information in agreement with detailed
information? For example, do all total fields equal the true total of the individual
fields?
Uniqueness – Is each
transaction, entity and event represented only once in the information? For Example,
are there any duplicate customers?
Timeliness? – Is the
information current with respect to the business requirements? For example, is
information updated weekly, daily, or hourly?
2. Define the relationship between a database and a database management
system.
A database maintains information about various types of objects (inventory), events (transactions), people
(employees) and places (warehouses).Typically, a given database has a structural description of the type of
facts held in that database: this description is known as a schema. In contrast to a database management
system (DBMS) which is a computer program used to manage and query a database. The properties and
design of database systems are included in the study of information science.
A database maintains information about various types of objects (inventory), events (transactions), people
(employees) and places (warehouses).Typically, a given database has a structural description of the type of
facts held in that database: this description is known as a schema. In contrast to a database management
system (DBMS) which is a computer program used to manage and query a database. The properties and
design of database systems are included in the study of information science.
3. Describe the advantages an organisation can gain by using a database.
A good database can handle changes quickly and easily, just as any good business needs to be able to
handle changes quickly and easily.
A good database can handle changes quickly and easily, just as any good business needs to be able to
handle changes quickly and easily.
The advantages and organisation can gain by using a database are as follows:
- Increased flexibility;
- Increased scalability and performance;
- Reduced information redundancy;
- Increased information integrity (quality);
- Increased information security;
4. Describe the benefits of a data-driven website.
- Development: Allows the website owner to make changes any time – all without
having to rely on a developer or
knowing HTML programming. A well-structured, data-driven website enables updating with little or no training.
knowing HTML programming. A well-structured, data-driven website enables updating with little or no training.
- Content management: A static website requires a programmer to make
updates. This adds an unnecessary
layer between the business and its web content, which can lead to misunderstandings and slow turnarounds for
desired changes.
layer between the business and its web content, which can lead to misunderstandings and slow turnarounds for
desired changes.
- Future expandability: Having a data-driven website enables the site to
grow faster than would be possible with a
static site. Changing the layout, displays and functionality of the site (adding more features and sections) is
easier with a data-driven solution.
static site. Changing the layout, displays and functionality of the site (adding more features and sections) is
easier with a data-driven solution.
Wednesday, 11 April 2012
Business Information Technology - Week Six Questions
What is information architecture and what is information infrastructure and how do they differ and how do they relate to each other?
Information architecture identifies where and how important information, such as customer records, is maintained and secured. Information Infrastructure includes the hardware, software and telecommunications equipment that, when combined, provides the underlying foundation to support the organisations goals. They differ in the way that information architecture only deals with the information that it is presented with and is responsible for how it is maintained and secured where as; information infrastructure deals with equipment perspective side that provides the underlying foundation to support the organisational goals. Each relates to one another in the way that they are both important in regards to the information that an organisation has within the business and equipment used to ensure everything is supported towards its goals.
Describe how an organisation can implement a solid information architecture
The three primary areas of information architecture are:
1) Backup and recovery; an organisation should choose a backup and recovery strategy that is in line with its business goals. If the organisation deals with large volumes of critical information, it will require daily backups, perhaps even hourly backups, to storage servers.
2) Disaster recovery; Considers the location of the backup information. Many organisations store backup information in an off-site facility, StorageTek, a worldwide technology company that delivers a broad range of data storage offerings, specialises in providing off-site information storage and disaster recovery solutions.
3) Information security; Security professional are under increasing pressure to do the job correctly and cost effectively as networks extend beyond organisations to remote users, partners and customers, and to mobile phone, PDAs and other mobile devices.
List and describe the five requirement characteristics of infrastructure architecture.
1) Flexibility – Systems must be flexible enough to meet all types of business changes. When the company starts growing and performing business in new countries, the system will already have the flexibility to handle multiple currencies and languages.
2) Scalability – Refers to how well a system can adapt to increased demands.
3) Reliability- Ensures all systems are functioning correctly and providing accurate information. Reliability is another term for accuracy when discussing the correctness of systems within the context of efficiency IT metrics.
4) Availability – Addresses when systems can be accessed by users.
5) Performance- Measures how quickly a system performs a certain process or transaction (in terms of efficiency IT metrics of both speed and throughput).
Describe the business value in deploying a service oriented architecture
Service oriented Architecture, with its loosely coupled nature, allows enterprises to plug in new services or upgrade existing services in a granular fashion. This enables businesses to address the new business requirements, provides the option to make the services consumable across different channels and exposes the existing enterprise and legacy applications as services, thereby safeguarding existing IT infrastructure investments.
What is an event?
Events are the eyes and ears of the business expressed in technology – they detect threats and opportunities and alert those who can act on the information.
What is a service?
Services are more like software products than they are coding projects. They must appeal to a broad audience, and they need to be reusable if they are going to have an impact on productivity.
Business Information Technology - Week Five Questions
Explain
the ethical issues surrounding information technology
Ethics is a system of moral principle that
considers our actions from right and wrong. Ethical issues surrounding informational
technology consist of the following
-Intellectual property: collection of rights that protect creative and intellectual
effort.
-Copyright:
Exclusive right to do certain acts with intangible property
-Fair use
doctrine:
In certain situations, it is legal to use copyrighted material
-Pirated
software:
unauthorized use, duplicate, distribution, or sale of copyrighted software.
-Counterfeit
software: software that is manufactured to look like the real thing and sold as
such
Describe a
situation involving technology that is ethical but illegal
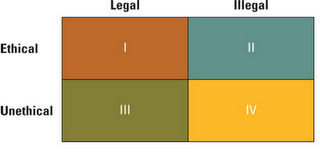 A situation involving technology that is ethical but
illegal may be; when one purchases a program for their computer and creates a backup
copy in case of any damage or loss of the original. Even though it states that
copies of the program are illegal and should not be made the backing up of a program
for your own use is not cheating the procedures of customers. This situation is
most definitely considered unethical if the copy is being made multiple times
to sell over the internet or at a market then the issue becomes both unethical
an illegal.
A situation involving technology that is ethical but
illegal may be; when one purchases a program for their computer and creates a backup
copy in case of any damage or loss of the original. Even though it states that
copies of the program are illegal and should not be made the backing up of a program
for your own use is not cheating the procedures of customers. This situation is
most definitely considered unethical if the copy is being made multiple times
to sell over the internet or at a market then the issue becomes both unethical
an illegal.
Describe and explain one of the
computer use policies that a company might employ
A company may employ an ‘internet use policy’ to contain
general principles to guide the proper use of the internet. This has some
unique aspects that make it a good candidate for its own policy. Implementing
this policy means that all employees are encouraged to use the internet
responsibly. These policies include:
1. Describe available internet services
2. Define the purpose and restriction of Internet access
3. Complements the ethical computer use policy
4. Describes user responsibilities
5. States the ramification for violations
1. Describe available internet services
2. Define the purpose and restriction of Internet access
3. Complements the ethical computer use policy
4. Describes user responsibilities
5. States the ramification for violations
What are the 5 main technology
security risks?
1) Human Error: after complete recheck to find any mistakes
2) Natural Disasters: regularly save data as back up and in alternative
area
3) Technical Failures: install a trustworthy spyware fighter and regularly
save data in a separate
4) Deliberate Acts: constantly monitor the employees actions when working
in the firm
5) Management Failure: Ensure proper training and procedures in the
workplace to new employees

Outline one way to reduce risk
One way to reduce risk may include ‘The second line of
defence technology.’ Organisations can deploy numerous technologies to prevent
information security breaches. When determining which types of technologies to
invest in, it helps to understand the three primary information security areas:
1 ) authentication and authorisation
2) Prevention and resistance
3) Detection and response
What is a disaster recovery plan,
what strategies might a firm employ?
A disaster recovery plan examines those situations that
prevent you from carrying on business. Disaster Recovery is a process of
regaining access to computer systems and data after a disaster has taken place.
Careful planning helps your business get back to normal operations as quickly
as possible. A firm might employ the following strategies.
-
location of backup
data: offsite data kept in order
-
Develop information security policies
-
Communicate the information security policies
-
Identify critical information assets and risks
-
Obtain stakeholder support
Saturday, 24 March 2012
Business Information Technology - Week Four Questions
1. What is Web 2.0, how does it differ from 1.0?
Web 2.0 is a set of economic, social and technology trends that collectively form the basis for the next generation of the internet – a more mature, distinctive medium characterised by user participation, openness and network effects. 2.0 is a more innovative, faster and modern version of 1.0.
2. How could a web 2.0 technology be used in business?
According to one commentator, ‘Web 2.0 is the business revolution in the computer industry caused by the move to the internet as platform, and an attempt to understand the rules for success on that new platform. It has been used in business as a transformative force that is propelling companies across all industries towards a new way of doing business
3. What is eBusiness, how does it differ from eCommerce?
EBusiness, derived from e-commerce, is the conducting of business on the Internet, including buying and selling, serving customers and collaborating with business partners. The primary difference between e-commerce and e-business is that e-business also refers to online exchanges of information, such as manufacturer allowing its suppliers to monitor production schedules or a financial institution allowing its customers to review their banking, credit car and mortgage accounts.
4. What is pure and partial eCommerce?
— Pure vs. Partial EC
--The product can be physical or digital.
--The process can be physical or digital.
--The delivery agent can be physical or digital.
— Brick-and-mortar organizations are purely physical organizations.
— Virtual organizations are companies that are engaged only in EC. (Also called pure play)
— Click-and-mortar organizations are those that conduct some e-commerce activities, yet their business is primarily done in the physical world. i.e. partial EC.
5. List and describe the various eBusiness models
E-business models are an approach to conducting electronic business on the Internet. These transactions take place between two main entities- businesses and consumers. The e-business models are stated below:
- Business-to-business (B2B) Applies to businesses buying from and selling to each other over the internet.
- Business-to-consumer (B2C) Applies to any business that sells its products or services to consumers over the internet
- Consumer-to-business (C2B) Applies to any consumer that sells a product or service to a business over the internet
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) Applies to sites primarily offering goods and services to assist consumers interacting with each other over the internet.
6. List and describe the major B2B marketplace models?
Business-to-business (B2B) applies to businesses buying from and selling to each other over the internet. Electronic marketplaces, or e-marketplaces, are interactive business communities providing a central market where multiple buyers and sellers can engage in e-business activities. Each presents structures for conducting commercial exchange, consolidating supply chains, and creating new sales channels. Their primary goal is to increase market efficiency by tightening and automating the relationship between buyers and sellers. Those existing e-marketplaces allow access to various mechanisms in which to buy and sell a range of things, from services to direct materials. These transactions are generally conducted via extranet – (individual companies’ intranets connected together using high levels of network security (often using a virtual private network, or VPN).
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

